A pharmacy in a plant
Over the last decade scientific publications on Aloe have multiplied, mainly updating its potential with special emphasis on its activity, emollient and soothing for the digestive system, detoxifying for the body and for the well-being of the throat, integrating and completing the conventional approach to the various conditions and disorders that are particularly significant in today’s world.
Currently 160 active ingredients are known. The main constituent of Aloe is acemannan, a mucopolysaccharide
Aloe on the market
There are numerous Aloe-based preparations available, used on its own or in combination. One should preferably choose 100% Aloe gel juice, without added water, sugar or alcohol, with a high concentration of polysaccharides and possibly titrated in Acemannan, the molecule that most of Aloe’s beneficial properties are attributed to. The juice should be obtained from plantations farmed without the use of fertilizers or synthetic products, free from gluten residues and free from aloin. To eliminate aloin the leaves are harvested and manually sliced on site, removing the cuticle of the leaves, needles and tips, where aloin is mainly concentrated. Furthermore, the older the harvested plant, the lower its aloin concentration, until it is negligible in plants at least 5 years old.
Taking Aloe vera gel by general route is recommended in numerous conditions, for internal use it is useful for the well-being of the digestive system, carrying out an emollient and soothing action, or when one wishes to have a purifying action, while for external use it has an effective emollient and soothing action on the skin.

 Specchiasol
Specchiasol Specchiasol
Specchiasol Specchiasol
Specchiasol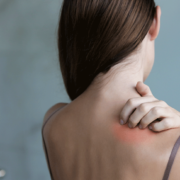 Specchiasol
Specchiasol Specchiasol
Specchiasol Specchiasol
Specchiasol



 Specchiasol
Specchiasol